Sleep plays a vital role in our overall health and well-being, and its impact extends beyond simply feeling rested. It turns out that sleep also influences our hunger and satiety hormones, ghrelin and leptin, which regulate appetite and energy balance. In this article , we will explore the fascinating relationship between sleep and these crucial hormones, shedding light on how sleep quality and duration affect ghrelin and leptin levels.
What are Ghrelin and Leptin?
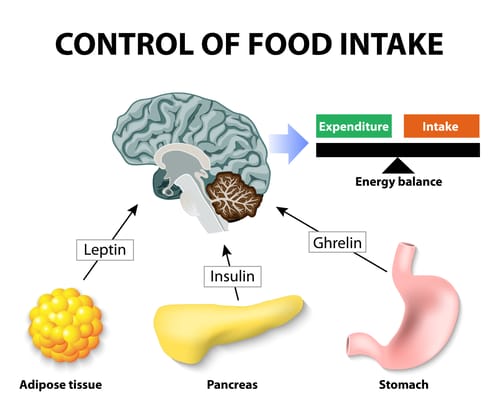
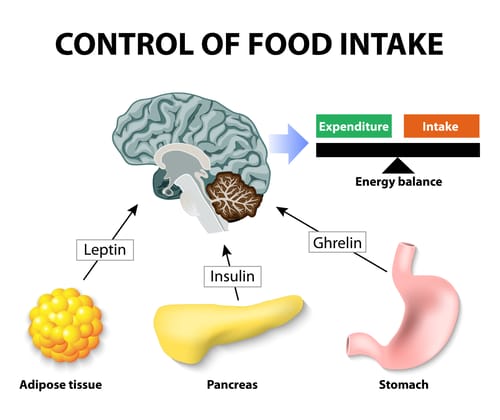
Ghrelin and leptin are two hormones that regulate hunger and satiety, respectively.
Ghrelin, often referred to as the “hunger hormone,” is produced primarily in the stomach and plays a role in stimulating appetite. It is released when the stomach is empty and its levels increase before meals, signaling hunger to the brain. Ghrelin acts on the hypothalamus, a region of the brain involved in appetite regulation, to stimulate the release of neuropeptides that increase food intake. It also affects other brain areas associated with reward and motivation, influencing food-seeking behavior. Ghrelin levels decrease after eating and are suppressed by the intake of nutrients.
Leptin, on the other hand, is known as the “satiety hormone” and is produced primarily by fat cells. Its levels increase as fat stores increase. Leptin acts as a signal to the brain, particularly the hypothalamus, to suppress appetite and increase energy expenditure. When fat stores are sufficient, leptin levels rise, leading to a decrease in appetite and an increase in metabolism. However, in cases of leptin resistance, which can occur in obesity, the body becomes less responsive to the signals of leptin, leading to continued hunger and overeating.
Both ghrelin and leptin are part of a complex network of hormones and signals that regulate appetite, energy intake, and energy expenditure. Imbalances or dysregulation of these hormones can contribute to conditions such as obesity, overeating, and other metabolic disorders. Understanding the roles of ghrelin and leptin has been a subject of significant research in the field of appetite regulation and obesity management.
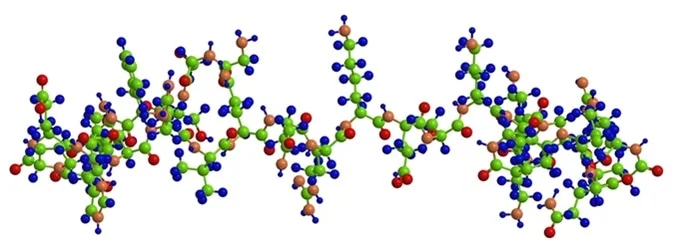
Hormone ghrelin (yellow) from crystal structure 1M04 in spacefill.
Protein leptin (coral) with four molecules of zinc (grey) from PDB 1AX8.
Role of Ghrelin and Leptin in Regulating Appetite
Ghrelin stimulates hunger by increasing food intake and promoting the storage of fat, while leptin suppresses appetite and burns fat. They work together to maintain energy balance and regulate food intake.
Ghrelin
- Stimulates appetite
- Promotes fat storage
- Increases food intake
Leptin
- Suppresses appetite
- Burns fat
- Regulates body weight
The Relationship between Sleep and Ghrelin/Leptin Levels
Sleep deprivation can negatively affect ghrelin and leptin levels, leading to an increase in appetite and a greater risk of obesity.
Studies have shown that lack of sleep can increase ghrelin levels and decrease leptin levels, resulting in an increase in appetite and a higher risk of overeating. Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to long-term imbalances in these hormones, which can negatively impact weight management and overall health.

A good night’s sleep is crucial to regulating hormones and managing appetite.
Studies Supporting the Link between Sleep and Ghrelin/Leptin
Research has demonstrated a clear link between sleep and ghrelin/leptin levels and their effects on appetite.
A study conducted by the University of Chicago found that subjects who slept for only 4 hours had a 28% increase in ghrelin levels and an 18% decrease in leptin levels, resulting in an increased appetite and a greater desire for calorie-dense foods.
| Study | Findings |
| University of Chicago | 4 hours of sleep led to increases in ghrelin and decreases in leptin, resulting in increases in appetite and food cravings. |
| University of Wisconsin-Madison | Sleep restriction resulted in a higher intake of calories and greater fat consumption. |
| Harvard Medical School | Average sleep duration was strongly associated with weight gain and obesity. |
Practical Tips for Better Sleep to Regulate Appetite
By adopting healthy sleep habits, you can regulate your ghrelin and leptin levels, and increase your chances of successful weight management.
Set a consistent bedtime and waking time
Establishing a regular sleep pattern can regulate your body clock and improve sleep quality.
Create a bedtime routine
Activities like reading or taking a relaxing bath can prepare your mind and body for sleep.
Avoid electronic devices before bedtime
Electronic screens emit blue light, which can suppress melatonin production and interfere with sleep.
Avoid caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime
Caffeine is a stimulant that can make it difficult to fall asleep, while alcohol can disrupt sleep patterns and decrease sleep quality.
Sleep plays a critical role in the regulation of ghrelin and leptin levels, and ultimately, in maintaining a healthy weight.
By utilizing the practical tips outlined in this guide, you can establish healthy sleep habits that will help regulate your appetite and improve your overall health.